Hemp-derived CBD products have shown potential in providing relief against a variety of symptoms and conditions. It is quite ironic that cannabis, once criminalized and neglected, is being given so much recognition by wellness enthusiasts around the world. Have cannabis-derived products worked for you? If yes, then you must have wondered about the reason behind their unparalleled therapeutic value.
The cannabis plant contains hundreds of different compounds, each with a benefit of its own. Nevertheless, two distinct plant compounds, produced in the same glands as each other, contribute to its much-needed therapeutic effects. These compounds are known as cannabinoids and terpenes, respectively.
If you are new to cannabis, you must be thinking:
What are cannabinoids, and;
Why are they so important?
Well, in this article, we will be exploring some cannabis chemistry so that you get a better understanding of how cannabinoids work. We will cover different types of cannabinoids, how they interact with our body through the endocannabinoid system, their benefits, effects, and much more. By the end, you will be able to educate others as well about how CBD and related compounds can be beneficial for people affected by difficult to manage conditions.
Let’s dive right in.
What Exactly is A Cannabinoid?
The next time you take a few drops of your favorite CBD tincture, make sure you know that the cannabinoid inside is providing you with pain relief and much of the product’s healing properties. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of our body, a complex system of cannabinoid receptors and receptor proteins that regulates essential bodily functions and mediates communication between cells.
Scientists are still trying to understand this intricate system, and we need more evidence to support the claims companies are making about the health benefits of these cannabinoids. However, with the limited research that we do have, it seems imminent that these lipophilic compounds have more to offer to the wellness community than we think. Cannabinoids come with numerous health benefits, and they can alleviate symptoms of several conditions, including pain, nausea, anxiety, stress, insomnia, etc.
Based on whether their synthesis occurs outside or inside the body, we can divide these cannabinoids into two different categories. These include endogenous cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids.
Endogenous Cannabinoids or Endocannabinoids
Don’t get confused! Endogenous is just a fancy term for anything that originates within the body. The human body is capable of synthesizing cannabinoids on its own, and these are known as endogenous or endocannabinoids. Our cells can produce these endocannabinoids on-demand from fatty acids present within the cell membranes. Endocannabinoids act as chemical messengers in our body to regulate immune response, inflammation, the transmission of pain, cell growth, and much more.
There are two primary endocannabinoids produced by the body, called anandamide and 2-AG. Both these compounds bind with CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system and are responsible for impacting most of its activity. However, there are other less significant endocannabinoids as well that contribute to smaller ECS activity in the muscle tissues.
Anandamide
Anandamide is the most abundant of all endocannabinoids found in the body since it is present in virtually every tissue. It is considered the primary compound that regulates ECS activity and is more prominently present in organs outside the brain. The term anandamide comes from the Sanskrit word for bliss or “ananda.” Adequate levels of anandamide in the body may promote a sense of calmness and satisfaction, probably the reason why it is called anandamide in the first place.
2-AG
2-AG is another primary endocannabinoid found in the human body that is responsible for a large portion of ECS activity in the central nervous system. It is a full agonist of the CB1 receptor, meaning it can bind with it and produce a biological response.
Exogenous Cannabinoids or Phytocannabinoids
Since phytocannabinoid are exogenous cannabinoids, their synthesis takes place outside the body. The cannabis plant is the primary source of phytocannabinoids. It contains more than 114 different types of these compounds, and their synthesis occurs in the resin glands or trichomes present on the plant’s surface.
The two most prominent phytocannabinoids derived from cannabis are THC and CBD, and they are the most widely used as well. THC is the psychoactive compound of the marijuana plant, known for producing intoxicating effects on its user. Comparatively, CBD does not show any psychoactive properties, and users have reported feeling calm and relaxed instead.
Are Cannabinoids Legal?
Considering how cannabis and its derivates have had a shaky relationship with the law, you must have the right knowledge about the legality of cannabinoids in your state before you buy any related products. Hemp-derived cannabinoid products that contain less than 0.3% THC are legal in the United States. Medical and recreational marijuana is also legal in some states, but you should check with local authorities if you don’t want any trouble.
Furthermore, people who get drug-tested regularly by their employer companies should avoid using products containing any cannabinoids. Firstly, there are full-spectrum CBD products out there with traces of THC that show up in drug tests. Secondly, not all third-party lab reports from cannabis companies are accurate, and your boss might not like how your drug test turns out if you are using products from any of these companies. All in all, do your research before you decide to opt for any cannabis product.
The Endocannabinoid System – How Do Cannabinoids Interact With Our Body?
Cannabinoids are known to be the foundation of the healing properties of cannabis. But, how do these compounds exert such a significant influence on our bodily functions? The answer is quite simple – the Endocannabinoid System. The role of ECS is more than just regulating how we experience the intoxicating properties of cannabis. It is an intricate system of receptors distributed carefully around the central and peripheral nervous system. The ECS regulates several essential physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain, memory, sleep, etc., and maintains balance or homeostasis in the body.
Although our body produces endocannabinoids of its own, sometimes the concentration of these compounds is not suitable enough to maintain a natural balance, which is why cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant allow the body to regain stability and ensure a smooth running of bodily functions.
Most cannabinoids bind with CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system. CB1 receptors are more abundant in the areas concerning the central nervous system, and they can regulate many brain functions. They also control the release of other neurotransmitters such as serotine, dopamine, and glutamate. Hence, the CB1 receptors are also responsible for the feeling of euphoria we get from cannabis.
On the other hand, CB2 receptors are present in immune cells that circulate the body through blood vessels. You can also find CB2 receptors on a few neurons in the brain region, and these are concerned with pain-relief, inflammation, and neuroprotection.
Cultivating A Healthy Internal Environment – The Therapeutic Value of Cannabinoids
The use of cannabinoids for their medicinal properties dates back thousands of years in the past. Several different cultures and religions have acknowledged the therapeutic value of the cannabis plant, including traditional Chinese medicine. Researchers believe that considering the amount of CB1 receptors currently present in an average human, it must have taken millions of years for endocannabinoid-signaling to evolve to this level.
Nevertheless, what scientists aim to achieve through the potential of cannabinoids as a medicine is the ability to connect them with the right cannabinoid receptors when they enter the body. With adequate concentrations of these compounds in the right regions, our body will have a lower probability of developing severe symptoms from a disease or chronic condition.
The thing with cannabis is that its therapeutic properties help the body cultivate a healthy internal environment by helping maintain better homeostasis. While we have limited scientific evidence to support all these claims, it does not mean that the therapeutic value of cannabinoids should go unnoticed. Cannabis affects every person individually, and whatever knowledge we do have about cannabinoids shows that combining them with extensive exercise and a balanced, nutritious diet might be the key to promoting an overall sense of wellness in your daily life.
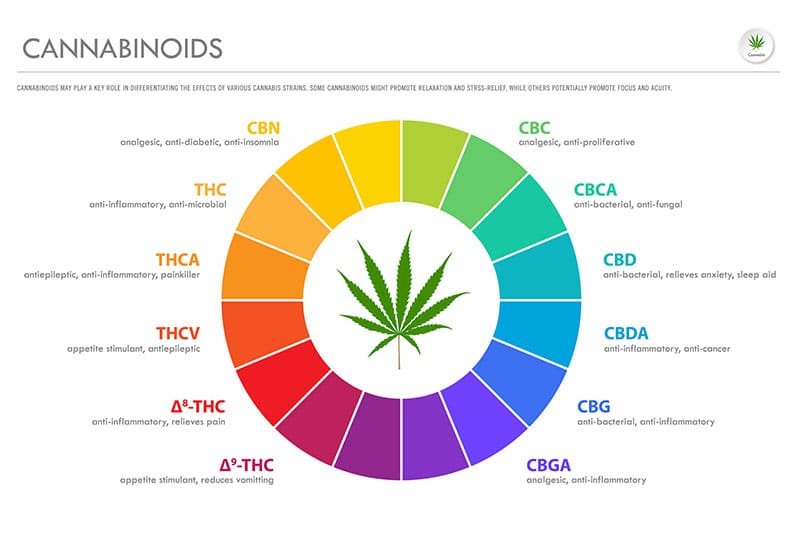
Cannabinoids Found in Hemp and Their Benefits
The hemp plant is a variant of the Cannabis Sativa plant and is consists of over 200 different cannabinoids. Different types of cannabinoids behave differently and can have varying effects on the body. It is crucial to know that most of these cannabinoids exist as acids in the hemp plant and require a certain amount of heat to become active. For example, CBD and THC exist as CBD-A and THC-A in the hemp plant before being processed into the right product.
Nevertheless, here are some of the primary cannabinoids found in the hemp plant and their benefits:
Cannabidiol (CBD)
Although cannabidiol is present in both hemp and marijuana variants of the cannabis plant, it is more abundant in the hemp plant, which is why companies usually get their CBD from it. It has calming and anxiety-relieving effects on its user. CBD may also reduce the unpleasant side effects of THC, including increased heart rate and intoxication. Moreover, evidence suggests that CBD can alleviate symptoms of a wide variety of conditions, including asthma, ADHD, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, etc. CBD is a natural analgesic and anti-inflammatory compound, which can also reduce stress and anxiety, making you feel a lot more composed. The FDA recently approved an oral suspension of CBD for the treatment of epilepsy in children. It is known as Epidiolex.
Cannabinol (CBN)
Cannabinol is a metabolite of THC when it breaks down into its constituent compounds. Plants that have gone through long periods of storage contain CBN in high concentrations. It is a non-psychoactive compound, which may have sedative properties.
Cannabigerol (CBG)
CBG is a less prominent cannabinoid found in plants harvested before they are fully ripe. It is becoming quite popular nowadays because of its supposed health benefits. CBG reduces intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients to relieve pain. A couple of animal studies have shown that CBG may also prevent dry-skin syndromes and keep the skin healthy. Moreover, it can also inhibit the growth of colon cancer in mice, according to a different animal study.
Cannabidivarin (CBD-V)
Since the concentration of cannabidivarin is relatively low in the cannabis plant, scientists consider it as a minor cannabinoid. Nevertheless, this cannabinoid has quite similar effects on the body as CBD. GW Pharmaceuticals, the company that developed Epidiolex, is conducting large scale clinical trials on the effectiveness of CBD-V against epilepsy.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THC-V)
Like THC, tetrahydrocannabivarin is a potent psychoactive substance. While we have limited evidence regarding its benefits, on-going studies are examining its effects on psychological conditions like PTSD. THC-V also exhibits anxiolytic properties, and some studies suggest that it might help treat symptoms of psychosis. Furthermore, a few animal studies suggest that it may decrease appetite as well.
Delta-9 Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol is one of the most prominent cannabinoids found in the marijuana plant. It interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system to trigger the release of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin plays a significant role in the psychoactive effects of this cannabinoid. Some studies have shown that THC may also possess pain-relieving properties and reduce nausea. Moreover, THC is a natural appetite stimulant and can give you the “munchies.”
Bottomline
It does not matter whether you are new to cannabis or a regular user. Understanding the mechanisms behind its healing properties is necessary for the people exploring it as a medicine. While the scientific evidence behind the therapeutic value of cannabinoids is limited, it doesn’t change the fact that the benefits of using them as a treatment for chronic conditions and diseases are unmatched.
Nevertheless, if you want to explore some of the best cannabis and hemp brands in the market, you can get started right now! Visit our shop and choose from several different premium quality products.
FAQs About Cannabinoids
Question: What do cannabinoids do to the body?
Answer: Cannabinoids bind to receptors belonging to the endocannabinoid system of our bodies. They can impact several bodily functions, including mood, appetite, sleep, memory, etc.
Question: Is CBD a cannabinoid?
Answer: Yes, CBD is one of the most prominent cannabinoids found in the hemp plant. It is non-psychoactive and comes with tons of therapeutic benefits for its user.
Question: What are examples of cannabinoids?
Answer: THC, CBD, CBN, THC-V are some examples of the phytocannabinoids found in the hemp plant. They all bind with CB1 and CB2 receptors present in our central and peripheral nervous systems.
Question: Does the human body have a cannabinoid system?
Answer: Yes, the human body does have an endocannabinoid system composed of cannabinoid receptors and receptor proteins that bind to neurotransmitters.
Question: How many types of cannabinoids are there?
Answer: There are two types of cannabinoids; endogenous cannabinoids that are produced in the human body and phytocannabinoids that are produced in the resin glands of the cannabis plant.